Information Disclosure
in line with TCFD recommendations
Under the "SAKATA INX VISION 2030," SAKATA INX Group has identified "strengthening our ESG and sustainability efforts by emphasizing the global environment and local community" as an important strategy, and has set "activities to maintain a sustainable global environment" as one of our material issues. We aim to create a society in which people can live safely and healthy by protecting the global environment.
For this purpose, we are working to solve societal issues and build a sustainable society through our business activities, such as reducing emissions of environmentally hazardous substances in our production activities and actively developing environmentally friendly products.
Information Disclosure in line with TCFD recommendations
We have expressed our support for the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) recommendations and joined the TCFD Consortium which is a forum for discussion among supporting companies and financial institutions. We will take this opportunity to further enhance our efforts to resolve various societal issues, including climate change, and actively promote information disclosure in line with the disclosure framework (Governance, Strategy, Risk Management, Metrics and Targets related to climate-related risks and opportunities) recommended by the TCFD.
Disclosure required by TCFD recommendations
| Governance | Strategy | Risk Management | Metrics and Targets | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirements | Disclose the organization's governance in regards to climate-related risks and opportunities | Disclose the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization's businesses, strategy and financial planning | Disclose how the organization identifies, assesses, and manages climate-related risks | Disclose the metrics and targets used to assess and manage relevant climate-related risks and opportunities, where such information is material |
| Governance | Disclose the organization's governance in regards to climate-related risks and opportunities | Strategy | Disclose the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization's businesses, strategy and financial planning | Risk Management | Disclose how the organization identifies, assesses, and manages climate-related risks | Metrics and Targets | Disclose the metrics and targets used to assess and manage relevant climate-related risks and opportunities, where such information is material |
|---|
1. Governance & Risk Management
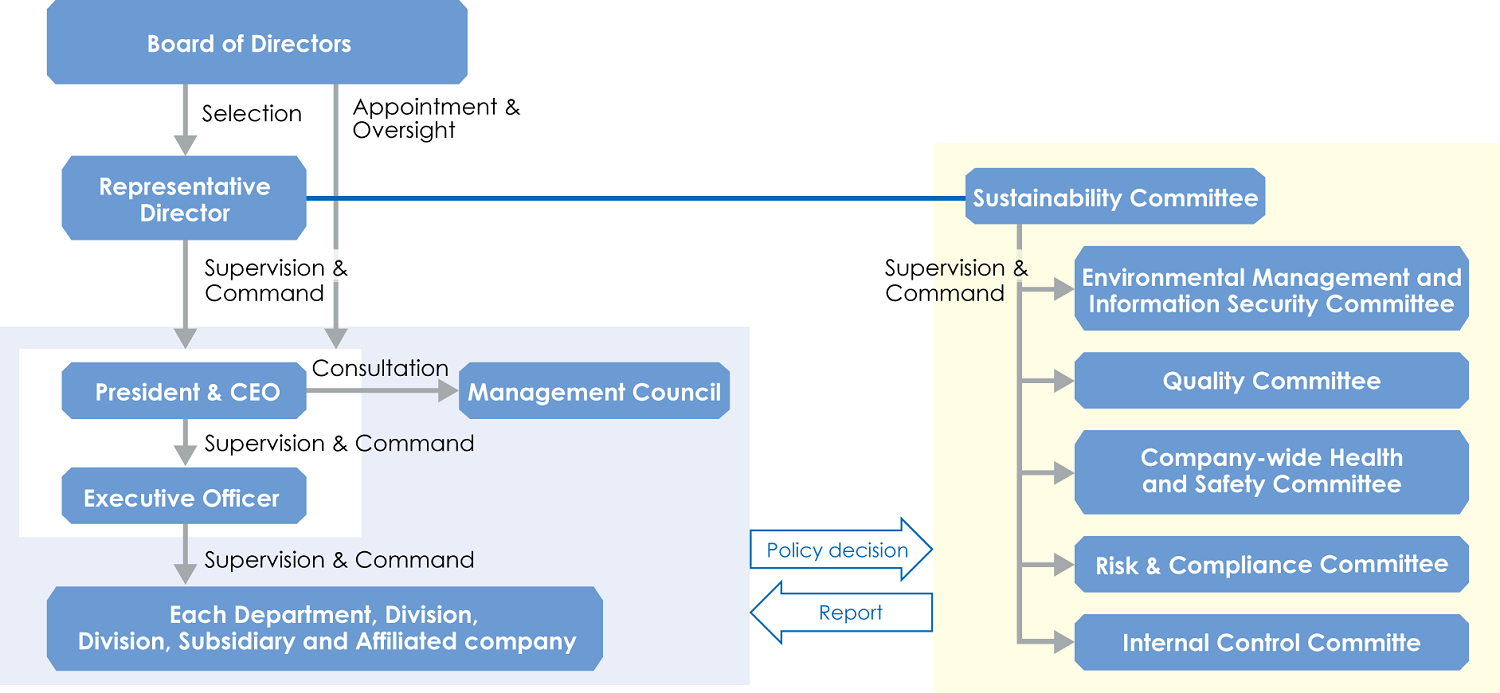
Climate change governance is overseen by the Sustainability Committee, which is chaired by the President & CEO and includes all members of the Board of Directors. In addition, various committees under the Sustainability Committee identify various risks, including our Group's response to climate change, and discuss measures on how to deal with them. The Sustainability Committee is held twice a year to approve important environmental policies and targets, including those related to climate change, and monitors its progress. In addition, the International Advisory Board also discusses issues related to climate change.
Risks related to climate change are identified by the Risk and Compliance Committee in accordance with the "Risk Management Policy," and a system is in place to prevent and respond to risks. Risks and countermeasures are monitored and periodically evaluated to review them accordingly to the situation.
▼Sustainability Promotion Structure including Climate Change Response
2. Strategy
SAKATA INX Group regards risks and opportunities associated with climate change to be the most important management challenge and recognizes that it will have significant impacts on our businesses. We have analyzed transition risks and opportunities under the 1.5℃ scenario and physical risks and opportunities under the 4℃ scenario, and have also been advancing measures to address them by referring to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), an international research organization, and the World Energy Outlook 2022 of the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other information.
In the scenario of limiting the increase in global average temperature to 1.5℃ compared to pre-industrial levels, our business may be affected by increased costs and decreased sales due to the strengthening of various laws and regulations and changes in the market as we transition to a low-carbon, decarbonized society. In response to those risks, the Group has set reduction targets for greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 & 2) and is continuously implementing measures to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. These include efforts to improve production efficiency, energy visualization, energy-saving activities, and the introduction of renewable energy. In addition, we see the growing demand for botanical inks that contribute to a low-carbon, recycling-oriented society, and functional coating agent products such as gas barrier agents for packaging as an opportunity for our Group to expand its businesses.
In the scenario where the average global temperature increases by 4℃ compared to pre-industrial times, our business could be affected by increased costs due to physical risks such as plant shutdowns, damage, supply chain disruptions caused by typhoons, torrential rains, floods and other natural disasters due to extreme weather conditions. In response to such risks, we are strengthening our global BCP, Business Continuity Plan. In addition, SAKATA INX Group sees opportunities to expand its businesses in the rise of demand for packaging inks due to growing demand for drinking water caused by the spread of heat stroke, and increased demand for antibacterial and antiviral products due to the rise in infectious diseases.
In this way, the Group views climate change not only as a risk but also as an opportunity, and aims to solve societal issues through its business activities.
Scenario Analysis Results
| Assumed timeframe: | to 2050 |
| Reference scenario: | 4℃ scenario IPCC/RCP8.5 |
| 1.5 / 2℃ scenario IPCC/RCP2.6, IEA/SDS,APS,NZE | |
| Time horizon: | Short-term:1-3 years |
| Medium-term:3-10 years | |
| Long-term:10-30 years | |
| Scenarios to be analyzed: | Existing and new projects |
Risks arising from the transition to a decarbonized society (1.5℃ scenario)
| Transition Risks | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy and Legal | Increase in carbon tax | Medium | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Increase in the ratio of in-house power generation through the introduction of renewable energy such as solar panels
・Introduced solar power generation at Shiga Plant and Tokyo Plant ・Considering further introduction of renewable energy in the future ◆Promoting energy conservation activities ・Improvement in productivity by continuous and further TPM activities (e.g. improvement in efficiency of production facilities and review of production conditions) ・Improvement in boiler efficiency ・Optimization of air conditioning temperature and enhancement in efficiency ・Reduction in electricity and gasoline consumption at non-production sites ◆Strict information security measures ・Computer virus countermeasures and access restricted to internal networks ・Investigation to improve energy security through cyber security measures |
| ・Increase in the cost of carbon taxes if reduction targets for greenhouse gas emissions are not met | |||||
| Increase in investment amounts and renovation costs for low carbonization of new and existing facilities | Medium | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in installation costs for photovoltaic systems | |||||
| Increase in cost of purchasing carbon credits under the Emissions Trading Scheme | Small | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in the cost of purchasing emission credits to achieve greenhouse gas emission reduction targets | |||||
| Increase in logistics costs due to CO2 emissions from ICE-equipped vehicles | Medium | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in cost of carbon tax on emissions from ICE-equipped vehicles
・Increase in capital costs for electrified vehicles and charging facilities |
|||||
| Plant shutdowns due to cyber-attacks on power grids such as photovoltaics | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales due to plant shutdowns |
| Market | Decrease in market competitiveness due to delayed decarbonization | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Developing and selling environmentally-friendly inks (e.g. botanical inks, inks made from recycled materials, etc.)
・Expansion in lineup of botanical products ・Product development aimed at increasing the proportion of plant-derived components ◆Building a resource recycling system that contributes to a recycling-based society ・Demonstrative testing to build a circular system from waste collection to treatment and resource recycling in printing-related industries, with the goal of creating a circular economy ◆New business development (environmental and biochemical fields) ・Development of biomass-based functional materials that help reduce GHG emissions ◆Mitigating the impact of raw material price fluctuation risk ・Paying close attention to raw material price trends ・Reduction in the use of petrochemicals ・Concentration of procurement sources and conclusion of long-term contracts ・Reduction in raw material costs and ensure stable supply through multiple sourcing, global procurement, etc. |
| ・Decrease in market competitiveness and decline in sales if the development of products that contribute to decarbonization is delayed |
|||||
| Rise in raw material prices | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| -Impact of introduction of carbon tax
・If the carbon tax for CO2 emissions of purchased products (raw materials) in Scope 3 Category 1 is added to the cost of raw materials, the costs will increase |
|||||
| -Uncertainty in the supply of raw materials due to the expansion of the biomass market
・Increase in costs of products using biomass feedstocks |
Large | High | Medium term | ||
| -Uncertainty in the supply of fossil fuel and soaring prices
・Increase in costs of products using petroleum-derived feedstocks |
Large | High | Medium term | ||
| -Rise in raw material prices due to greater reuse, etc.
・Increase in costs of our applicable products due to the use of recycled materials |
Large | High | Medium term |
| Techno- logy |
Conversion to Low-Energy Printing | Large | High | Medium term | ◆Development of low energy printing inks
・Development of EB curable inks ・Development of UV-curable inks ・Development of UV-curable inkjet inks ◆Response to paper packaging ・Development of gas barrier coating agents ・Development of heat sealants ・Development of functional coating materials such as moisture-resistant, water-resistant, oil-resistant, water repellent, slip-proof, etc. |
| ・If the development and commercialization of products suitable for low-energy printing is delayed, sales will decrease due to lost business opportunities | |||||
| Expansion of paper recycling | Large | High | Short term | ||
| ・If the development and commercialization of products that are compatible with recycled paper is delayed, sales will decrease due to loss of business opportunities | |||||
| Decrease in printed area | Large | High | Short term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of inks used on labels due to the shift to label-less printing
・Decrease in sales of packaging inks |
| Reputation | Loss of reputation from investors due to failure to address climate change and disclose information | Medium | Medium | Medium term | Promoting Proactive Responses to Climate Change
Appropriate disclosure of TCFD-related information |
| ・Decrease in market capitalization if stock prices drop due to lower valuation from investors |
Risks from physical impacts such as disasters due to climate change and others (4℃ scenario)
| Physical Risks | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Plant shutdowns, supply chain disruptions and infrastructure damage due to natural disasters | Large | High | Medium term | ◆Enhance global BCP responses
・Building a supply system from alternate locations and conduct training ・Building a BCP structure that utilizes a global network ◆Conducting regular surveys using the water risk assessment tool "Aqueduct" ・Initiate surveys on water risks (e.g. risks related to quantity and quality, floods, droughts, water stress, etc.) and consider responses, including future projections |
| ・Decrease in sales due to plants shutdowns caused by flooding
・Damage to plant facilities caused by flooding ・Increase in costs for flood and water damage control |
|||||
| Decrease in consumer activity due to significant restrictions on people's lives from natural disasters | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of our products due to reduced consumer activity |
| Chronic | Plant shutdowns due to rise in sea level | Large | Medium | Long term | ◆Monitoring the information in the IPCC Assessment Report
◆Regular surveys using the Climate Change Knowledge Portal (CCKP) ・Regular monitoring of extremely hot days and changes in rainfall ◆Preventing deterioration of the working environment due to rising temperature ・Continuous improvement in the working environment based on feedback from each workplace ◆Collect information on materials overall ◆Mitigate the impact of raw material prices fluctuation risks ・Same as Transition Risk【market】 ◆Promotion of biodiversity conservation activities ・Establishment of Basic Policy on Biodiversity ・Participation in the "30by30 Alliance" ・Participation in the "Clean Ocean Material Alliance (CLOMA)" ・Biodiversity risk assessment (conducting a survey using IBAT and reviewing the situation around each site) |
| ・Increase in costs for countermeasures at low-lying bases in Japan and overseas | |||||
| Increase in cost for countermeasures, productivity loss due to rise in average temperature | Large | High | Long term | ||
| ・Increase in equipment costs for heat stroke countermeasures
・Decrease in worker productivity due to increase in heat stroke and infectious diseases |
|||||
| Soaring cost of plant-derived raw materials | Large | Medium | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in costs of products containing plant-based raw materials | |||||
| Soaring cost of petroleum-derived raw materials | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in costs of products containing petroleum-derived raw materials | |||||
| Unstable supply of raw materials for paper due to frequent forest fires | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of applicable inks due to decline in paper and paper packaging consumption | |||||
| Decrease in Agricultural, Seafood, etc. | Large | Medium | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of our packaging inks |
Business opportunities (▮1.5℃ scenario, ▮4℃ scenario)
| Opportunities | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Efficiency | ▮Building a business scheme around the reuse of plastics | Large | High | Medium term | ◆>Participation in "R Plus Japan Co., Ltd." and "Japan Circular Economy Partnership (J-CEP)"
・Development of washable inks ・Development of recyclable film seperating materials |
| ・Increase in sales of our compatible products |
| Energy Source |
▮Improvement in energy efficiency through electrification and energy conservation measures | Medium | High | Medium term | ◆Increase in the ratio of in-house power generation through the introduction of renewable energy such as solar panels
・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 ・◆Promotion of energy conservation activities ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 |
| ・Reduction in energy intensity through CO2 reduction measures | |||||
| ▮Reducing CO2 emissions by introducing renewable energy | Small | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Reducing the cost of carbon taxes by introducing renewable energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions |
| Products and Services | ▮▮Expansion of environmentally-friendly products | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Development of inks for recycled packaging that support SDGs
・Development of gas barrier coating agent series ・Development of functional coating material series ・Research to improve the ratio of plant-derived components in botanical inks ・Development of water-based inkjet inks and UV-curable inks |
| ・Increase in sales of packaging inks due to increase in sales opportunities for paper packaging resulting from the elimination of plastics
・Increase in sales of barrier coating agents due to increase in sales opportunities for paper packaging resulting from the elimination of plastics ・Increase in sales of gas barrier agents, etc. due to growing demand for food preservation functions ・Increase in sales of products that help reduce CO2 emissions ・Increase in sales of energy-saving printing inks (e.g. inkjet inks, UV inks and EB inks) ・Increase in sales of products made from recycled materials ・Increase in sales of inks for recycled paper as paper recycling expands |
|||||
| ▮Expansion in the renewable energy and battery industries | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆New Business Development (Energy Chemicals and Electronic Chemicals businesses)
・Development of semiconductors and sensitizing materials for renewable energy applications such as solar cells ・Development of conductive materials, insulating materials, etc. that are expected to be used in the IoT and mobility fields |
|
| ・Increase in sales opportunities for energy chemical products
・Increase in sales opportunities for electronic chemical products |
| Markets | ▮Increase in heat stroke due to global warming | Large | High | Short to Long term | ◆Development of beverage packaging ink
・Development of flexo inks, gravure inks and metal decorating inks |
| ・Increase in sales of packaging inks due to increase in demand for drinking water | |||||
| ▮Increase in infectious diseases due to global warming | Small | Medium | Medium term | ◆Development of antibacterial and antiviral products | |
| ・Increase in sales of antibacterial and antiviral products |
| Resilience | ▮Enhance BCP responses | Medium | Medium | Medium term | ◆Enhance global BCP responses
・Same as Physical Risks【Acute】 ◆Installing solar panels and increasing the share of renewable energy in electricity generation ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 ◆Promotion of energy conservation activities ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 |
| ・Increase in stock prices due to improvement in customer confidence and investor valuation | |||||
| ▮Introduction of renewable energy and promotion of energy-saving measures | |||||
| ・Increase in stock prices due to improvement in customer confidence and investor valuation |
| Others | ▮Behavior change | Small | High | Short term | ◆Encouraging energy conservation activities
◆Encouraging behavior change towards decarbonization |
| ・Reduction of carbon tax costs through energy conservation activities, and reduction in CO2 emissions in Scope 3 Category 6 (business travel) and Category 7 (commuting) |
Risks arising from the transition to a decarbonized society (1.5℃ scenario)
| Transition Risks | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy and Legal | Increase in carbon tax | Medium | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Increase in the ratio of in-house power generation through the introduction of renewable energy such as solar panels
・Introduced solar power generation at Shiga Plant and Tokyo Plant ・Considering further introduction of renewable energy in the future ◆Promoting energy conservation activities ・Improvement in productivity by continuous and further TPM activities (e.g. improvement in efficiency of production facilities and review of production conditions) ・Improvement in boiler efficiency ・Optimization of air conditioning temperature and enhancement in efficiency ・Reduction in electricity and gasoline consumption at non-production sites ◆Strict information security measures ・Computer virus countermeasures and access restricted to internal networks ・Investigation to improve energy security through cyber security measures |
| ・Increase in the cost of carbon taxes if reduction targets for greenhouse gas emissions are not met | |||||
| Increase in investment amounts and renovation costs for low carbonization of new and existing facilities | Medium | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in installation costs for photovoltaic systems | |||||
| Increase in cost of purchasing carbon credits under the Emissions Trading Scheme | Small | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in the cost of purchasing emission credits to achieve greenhouse gas emission reduction targets | |||||
| Increase in logistics costs due to CO2 emissions from ICE-equipped vehicles | Medium | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in cost of carbon tax on emissions from ICE-equipped vehicles
・Increase in capital costs for electrified vehicles and charging facilities |
|||||
| Plant shutdowns due to cyber-attacks on power grids such as photovoltaics | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales due to plant shutdowns | |||||
| Market | Decrease in market competitiveness due to delayed decarbonization | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Developing and selling environmentally-friendly inks (e.g. botanical inks, inks made from recycled materials, etc.)
・Expansion in lineup of botanical products ・Product development aimed at increasing the proportion of plant-derived components ◆Building a resource recycling system that contributes to a recycling-based society ・Demonstrative testing to build a circular system from waste collection to treatment and resource recycling in printing-related industries, with the goal of creating a circular economy ◆New business development (environmental and biochemical fields) ・Development of biomass-based functional materials that help reduce GHG emissions ◆Mitigating the impact of raw material price fluctuation risk ・Paying close attention to raw material price trends ・Reduction in the use of petrochemicals ・Concentration of procurement sources and conclusion of long-term contracts ・Reduction in raw material costs and ensure stable supply through multiple sourcing, global procurement, etc. |
| ・Decrease in market competitiveness and decline in sales if the development of products that contribute to decarbonization is delayed |
|||||
| Rise in raw material prices | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| -Impact of introduction of carbon tax
・If the carbon tax for CO2 emissions of purchased products (raw materials) in Scope 3 Category 1 is added to the cost of raw materials, the costs will increase |
|||||
| -Uncertainty in the supply of raw materials due to the expansion of the biomass market
・Increase in costs of products using biomass feedstocks |
Large | High | Medium term | ||
| -Uncertainty in the supply of fossil fuel and soaring prices
・Increase in costs of products using petroleum-derived feedstocks |
Large | High | Medium term | ||
| -Rise in raw material prices due to greater reuse, etc.
・Increase in costs of our applicable products due to the use of recycled materials |
Large | High | Medium term | ||
| Techno- logy |
Conversion to Low-Energy Printing | Large | High | Medium term | ◆Development of low energy printing inks
・Development of EB curable inks ・Development of UV-curable inks ・Development of UV-curable inkjet inks ◆Response to paper packaging ・Development of gas barrier coating agents ・Development of heat sealants ・Development of functional coating materials such as moisture-resistant, water-resistant, oil-resistant, water repellent, slip-proof, etc. |
| ・If the development and commercialization of products suitable for low-energy printing is delayed, sales will decrease due to lost business opportunities | |||||
| Expansion of paper recycling | Large | High | Short term | ||
| ・If the development and commercialization of products that are compatible with recycled paper is delayed, sales will decrease due to loss of business opportunities | |||||
| Decrease in printed area | Large | High | Short term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of inks used on labels due to the shift to label-less printing
・Decrease in sales of packaging inks |
|||||
| Reputa- tion |
Loss of reputation from investors due to failure to address climate change and disclose information | Medium | Medium | Medium term | Promoting Proactive Responses to Climate Change
Appropriate disclosure of TCFD-related information |
| ・Decrease in market capitalization if stock prices drop due to lower valuation from investors |
Risks from physical impacts such as disasters due to climate change and others (4℃ scenario)
| Physical Risks | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Plant shutdowns, supply chain disruptions and infrastructure damage due to natural disasters | Large | High | Medium term | ◆Enhance global BCP responses
・Building a supply system from alternate locations and conduct training ・Building a BCP structure that utilizes a global network ◆Conducting regular surveys using the water risk assessment tool "Aqueduct" ・Initiate surveys on water risks (e.g. risks related to quantity and quality, floods, droughts, water stress, etc.) and consider responses, including future projections |
| ・Decrease in sales due to plants shutdowns caused by flooding
・Damage to plant facilities caused by flooding ・Increase in costs for flood and water damage control |
|||||
| Decrease in consumer activity due to significant restrictions on people's lives from natural disasters | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of our products due to reduced consumer activity | |||||
| Chronic | Plant shutdowns due to rise in sea level | Large | Medium | Long term | ◆Monitoring the information in the IPCC Assessment Report
◆Regular surveys using the Climate Change Knowledge Portal (CCKP) ・Regular monitoring of extremely hot days and changes in rainfall ◆Preventing deterioration of the working environment due to rising temperature ・Continuous improvement in the working environment based on feedback from each workplace ◆Collect information on materials overall ◆Mitigate the impact of raw material prices fluctuation risks ・Same as Transition Risk【market】 ◆Promotion of biodiversity conservation activities ・Establishment of Basic Policy on Biodiversity ・Participation in the "30by30 Alliance" ・Participation in the "Clean Ocean Material Alliance (CLOMA)" ・Biodiversity risk assessment (conducting a survey using IBAT and reviewing the situation around each site) |
| ・Increase in costs for countermeasures at low-lying bases in Japan and overseas | |||||
| Increase in cost for countermeasures, productivity loss due to rise in average temperature | Large | High | Long term | ||
| ・Increase in equipment costs for heat stroke countermeasures
・Decrease in worker productivity due to increase in heat stroke and infectious diseases |
|||||
| Soaring cost of plant-derived raw materials | Large | Medium | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in costs of products containing plant-based raw materials | |||||
| Soaring cost of petroleum-derived raw materials | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Increase in costs of products containing petroleum-derived raw materials | |||||
| Unstable supply of raw materials for paper due to frequent forest fires | Large | High | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of applicable inks due to decline in paper and paper packaging consumption | |||||
| Decrease in Agricultural, Seafood, etc. | Large | Medium | Medium term | ||
| ・Decrease in sales of our packaging inks |
Business opportunities (▮1.5℃ scenario, ▮4℃ scenario)
| Opportunities | Impacts to our businesses and financials | Magnitude of impact | Likelihood | Time Horizon | Our Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Efficiency | ▮Building a business scheme around the reuse of plastics | Large | High | Medium term | ◆Participation in "R Plus Japan Co., Ltd." and "Japan Circular Economy Partnership (J-CEP)"
・Development of washable inks ・Development of recyclable film seperating materials |
| ・Increase in sales of our compatible products | |||||
| Energy Source |
▮Improvement in energy efficiency through electrification and energy conservation measures | Medium | High | Medium term | ◆Increase in the ratio of in-house power generation through the introduction of renewable energy such as solar panels
・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 ・◆Promotion of energy conservation activities ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 |
| ・Reduction in energy intensity through CO2 reduction measures | |||||
| ▮Reducing CO2 emissions by introducing renewable energy | Small | High | Short to Medium term | ||
| ・Reducing the cost of carbon taxes by introducing renewable energy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions | |||||
| Products and Services | ▮▮Expansion of environmentally-friendly products | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆Development of inks for recycled packaging that support SDGs
・Development of gas barrier coating agent series ・Development of functional coating material series ・Research to improve the ratio of plant-derived components in botanical inks ・Development of water-based inkjet inks and UV-curable inks |
| ・Increase in sales of packaging inks due to increase in sales opportunities for paper packaging resulting from the elimination of plastics
・Increase in sales of barrier coating agents due to increase in sales opportunities for paper packaging resulting from the elimination of plastics ・Increase in sales of gas barrier agents, etc. due to growing demand for food preservation functions ・Increase in sales of products that help reduce CO2 emissions ・Increase in sales of energy-saving printing inks (e.g. inkjet inks, UV inks and EB inks) ・Increase in sales of products made from recycled materials ・Increase in sales of inks for recycled paper as paper recycling expands |
|||||
| ▮Expansion in the renewable energy and battery industries | Large | High | Short to Medium term | ◆New Business Development (Energy Chemicals and Electronic Chemicals businesses)
・Development of semiconductors and sensitizing materials for renewable energy applications such as solar cells ・Development of conductive materials, insulating materials, etc. that are expected to be used in the IoT and mobility fields |
|
| ・Increase in sales opportunities for energy chemical products
・Increase in sales opportunities for electronic chemical products |
|||||
| Markets | ▮Increase in heat stroke due to global warming | Large | High | Short to Long term | ◆Development of beverage packaging ink
・Development of flexo inks, gravure inks and metal decorating inks |
| ・Increase in sales of packaging inks due to increase in demand for drinking water | |||||
| ▮Increase in infectious diseases due to global warming | Small | Medium | Medium term | ◆Development of antibacterial and antiviral products | |
| ・Increase in sales of antibacterial and antiviral products | |||||
| Resilience | ▮Enhance BCP responses | Medium | Medium | Medium term | ◆Enhance global BCP responses
・Same as Physical Risks【Acute】 ◆Installing solar panels and increasing the share of renewable energy in electricity generation ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 ◆Promotion of energy conservation activities ・Same as Transition Risk【Policy and Legal】 |
| ・Increase in stock prices due to improvement in customer confidence and investor valuation | |||||
| ▮Introduction of renewable energy and promotion of energy-saving measures | |||||
| ・Increase in stock prices due to improvement in customer confidence and investor valuation | |||||
| Others | ▮Behavior change | Small | High | Short term | ◆Encouraging energy conservation activities
◆Encouraging behavior change towards decarbonization |
| ・Reduction of carbon tax costs through energy conservation activities, and reduction in CO2 emissions in Scope 3 Category 6 (business travel) and Category 7 (commuting) |
Quantitative assessment (1) [Financial impact of carbon taxes]
▮ Envisaged risks
Increased operating costs due to the increase in carbon pricing
▮ Standards for calculation
- Based on CO2 emissions in the baseline year (2022) for the SBT reduction target, we calculated for the cases where the target of a 58.8% reduction in the target year (2034) is not achieved, and where it is achieved.
- We used the 2030 carbon price for developed countries (140 USD) in the Net Zero Emission Scenario of the IEA's World Energy Outlook 2022. (Calculated at the 2022 rate of 1 USD = 110 yen)
- Scope 2 CO2 emissions were calculated based on location standards, but will be recalculated based on market standards in the future.
▮ Evaluation results
- Carbon tax burden in the target year (2034) if CO2 emissions do not change from the baseline year: 710 million yen
- Carbon tax burden in the target year (2034) if the STB standard reduction target is achieved: 290 million yen
→ If the reduction target is achieved, it will lead to a reduction of 420 million yen per year in operating costs.
▮ Response to reduce risks
- Energy-saving activities such as by improving production efficiency
- Introducing renewable energy
- Reducing our CO2 emission factor for emissions derived from electric power.
We will engage in the following:
Quantitative assessment (2) [Financial impact of flooding]
▮ Envisaged risks
Damage to plant equipment due to flooding and decline in sales due to plant shutdowns
▮ Standards for calculation
- Of all the Group's production locations, we conducted flood simulations for four plants in Japan and five plants overseas based on 1.5℃ and 4℃ scenarios with the cooperation of Gaia Vison, a University of Tokyo startup. These overseas plants were assessed as being at extremely high risk of river flooding using the Aqueduct 4.0 Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, a water risk assessment tool developed and published by the World Research Institute (WRI).
- We estimated the amount of financial impact based on the estimated rate of damage to facilities based on the calculated flood depth, and the number of days of business suspension.
▮ Evaluation results
In the 4℃ scenario, the financial impact of a once-in-a-century flood, is as follows.
* In Indonesia (Jakarta) and Thailand (Sinsakhon), the inundation depth in the event of a flood (considered to be a probability of once in 100 years) was analyzed to be 0m in the 4℃ scenario. It is not included in the financial impact.
▼In the 4℃ scenario, the financial impact of a once-in-a-century flood, is as follows.
| Japan | Equipment damage | Decrease in sales | Total financial impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Plants (Tokyo, Hanyu, Shiga, Osaka) |
5.783 billion yen | 7.257 billion yen | 13.04 billion yen |
| Overseas | Equipment damage | Decrease in sales | Total financial impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indonesia (Jakarta) | Inundation depth: 0m | ||
| Thailand (Sinsakhon) | Inundation depth: 0m | ||
| Thailand (Bangkok) | 1.422 billion yen | 0.611 billion yen | 2.033 billion yen |
| Vietnam (Hanoi) | |||
| Bangladesh (Dhaka) | |||
We will sequentially evaluate sites other than the above and update their information.
▮ Response to reduce risks
- Establishing a code of conduct in the event of storm and flood damage
- Stockpiling materials and equipment (sandbags and waterstops, etc.) to prevent flooding
- Establishing BCP regulations, and creating a BCM subcommittee
We are implementing various measures such as:
3. Metrics and Targets
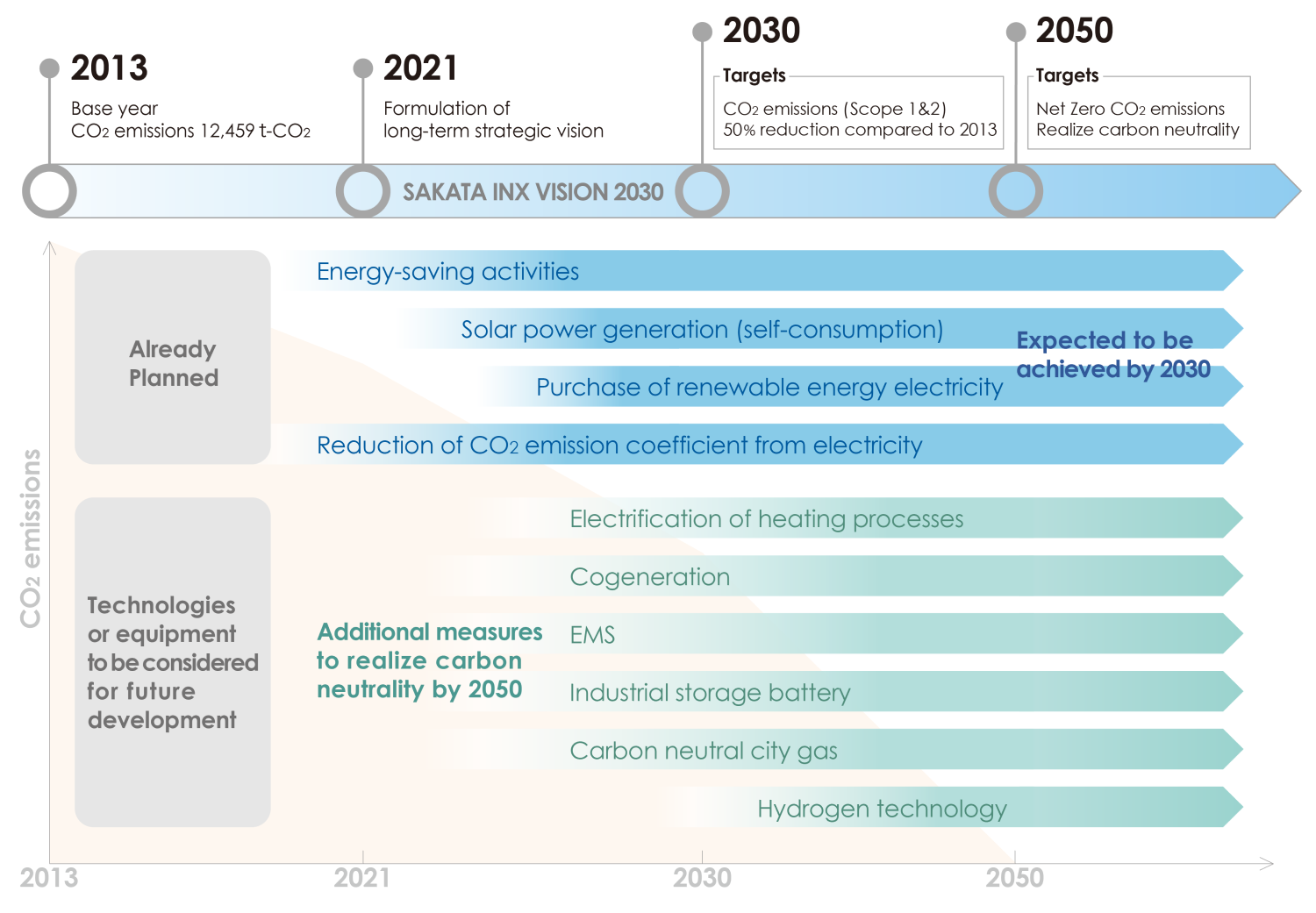
In the long-term strategic vision announced in 2021, we set a target of reducing greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1 & 2) in Japan by 50% by 2030 in comparison with FY2013. To achieve even greater results, we have decided to work to address SBTs, which are required to meet the level of the 1.5℃ target set in the Paris Agreement. The Group submitted a letter of commitment to the SBTi in 2023, and set a target of reducing Scope 1 & 2 emissions by 58.8% by 2034 in comparison with FY2022.
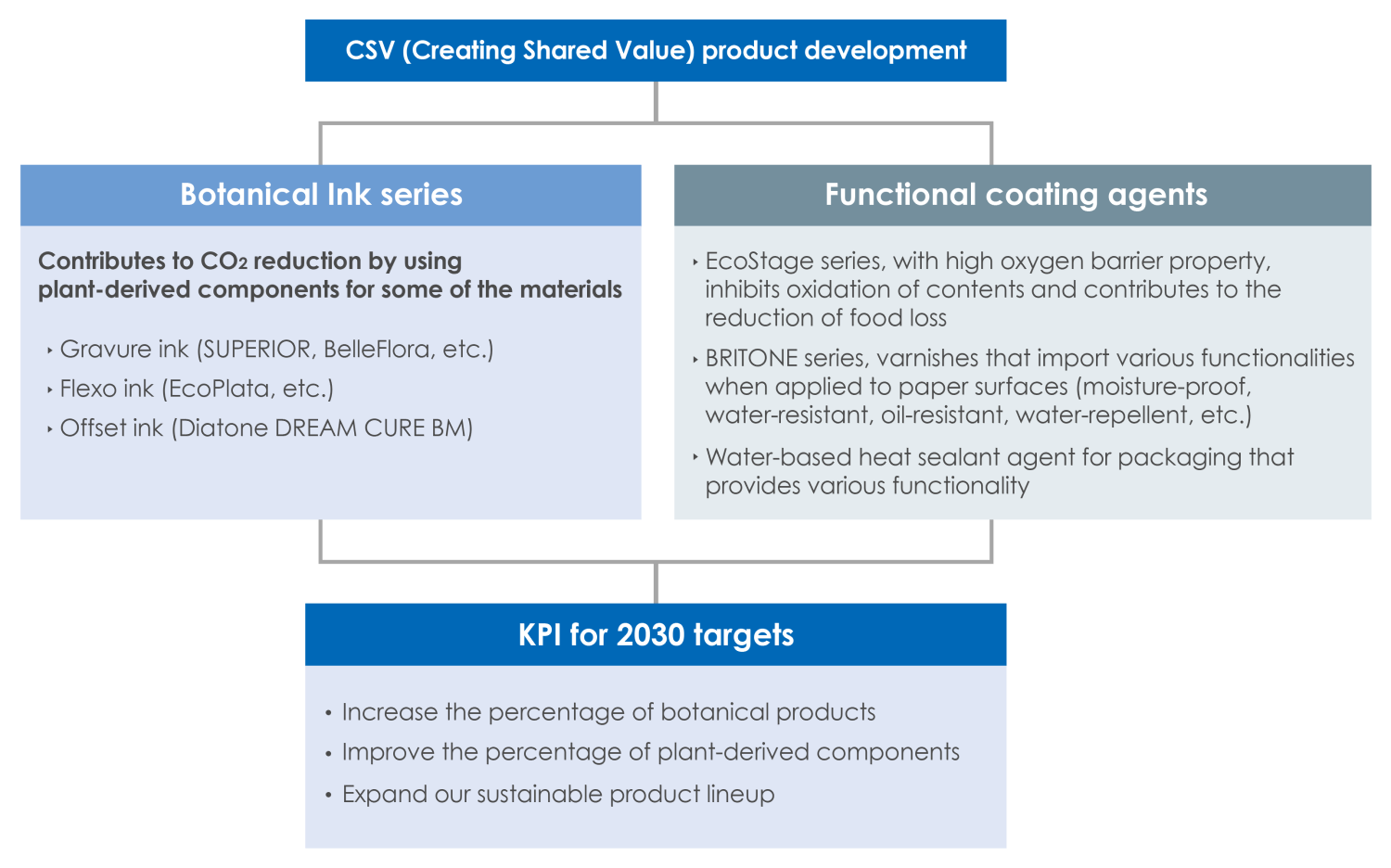
In addition, the key issue (materiality) is to strengthen research and development and technological capabilities. The individual issue within this is the development of CSV (Creation of Shared Value) products. For example, we have been promoting various initiatives by setting KPI to achieve our 2030 targets, such as increasing the proportion of botanical products using plant-derived components that contribute to a low-carbon society, and expanding our sustainable product lineup, such as functional coating agents (e.g., gas barrier agents) that contribute to a recycling-based society.
▼Our goal towards achieving the carbon neutrality
▼Contribution to the carbon neutrality of whole of society
Initiatives in Our Company
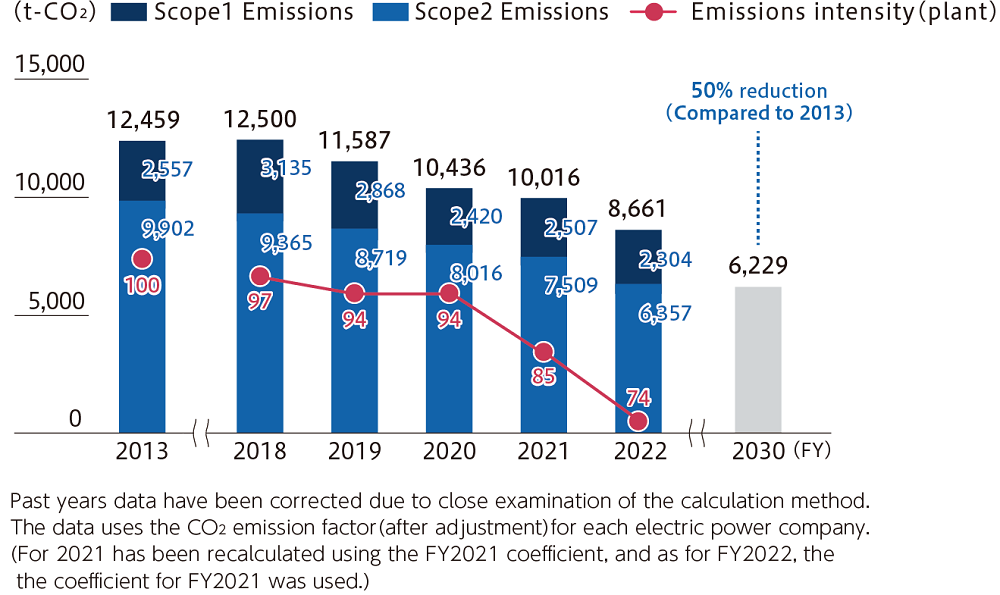
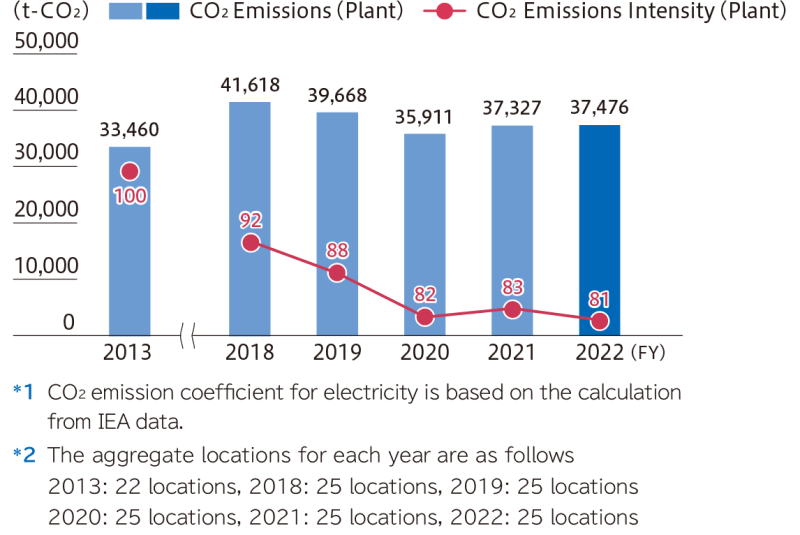
Our CO2 emissions (Scope1 & 2) resulting from energy use in FY2023 were 9,134 t-CO2 , which represents a 26.6% reduction compared to FY2013. The carbon intensity of our plants in that year was 88 if the intensity in FY2013 is taken to be 100. We have been working even more actively to promoting production efficiency and making improvements to save energy. We have introduced low-carbon electricity at our production sites and are working continuously to reduce electric power consumption, including at non-production sites.
▼CO2 Emissions (Japan) Trends and Targets

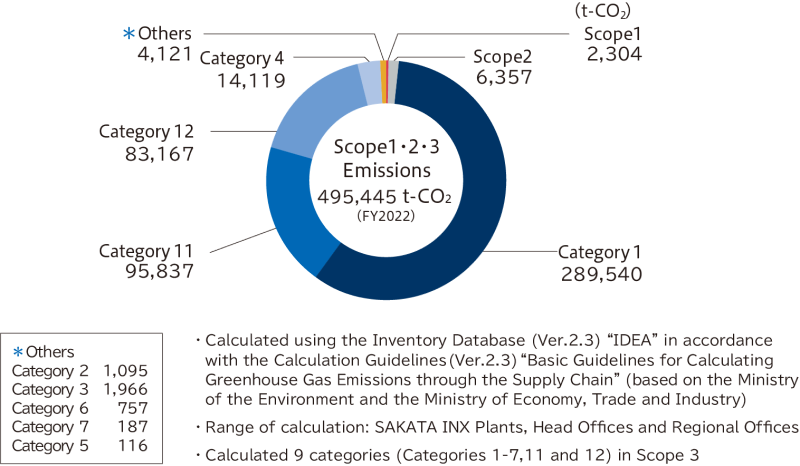
We have also calculated Scope 3 emissions in order to consider and implement the reduction of CO2 emissions in the supply chain. Since the proportion of Category 1 emissions (purchased goods and services) (approx. 72% in FY2022) and Category 12 emissions (end-of-life treatment of sold products) (approx. 21% in FY2022) is high, we will proceed with considerations for further reductions primarily in Category 1.
▼Supply chain emissions (Scope 3)

Initiatives in Our Group
We have set a target of reducing CO2 emissions (Scope 1 & 2) from our business activities by 58.8% (compared to FY2022) by FY2034 on a consolidated basis, and have launched initiatives to achieve this target. CO2 emissions from energy consumption in FY2023 were 41,394 t-CO2, constituting a 3.4% reduction in comparison with FY2022. Going forward, in order to achieve our target, we will increase use of renewable energy and reduce CO2 emissions throughout the Group, by increasing the numbers of solar panels and introducing new solar generation equipment at plants both in Japan and overseas.
▼CO2Emissions (Overseas) Trends *1~*2

The Group also introduced an ICP system for capital investments in FY2024. Going forward, we will drive low-carbon investments by utilizing the ICP system as one of the criteria for investment decisions, and will take steps to further reduce CO2 emissions, with a view to the creation of a decarbonized society.
<Overview of the ICP system>
| Internal carbon price: | 15,000 yen / t-CO2 |
| System coverage: | Capital investments accompanying changes in CO2 emissions |
| Operational procedures: | Internal carbon pricing is applied for CO2 emissions based on planned capital investments, and the conversion to a monetary amount is used as a reference for investment decision-making. |
4. Our products contributing to sustainability
With the aim of reducing CO2 emissions, greenhouse gas, we are developing inks that contain 10% or more plant-derived components in the ink solid content. The sales ratio of botanical inks for film packaging in Japan have increased to nearly 60%, and awareness of the series is spreading among printers, converters, some brand owners and consumers. We will continue to strengthen overseas deployment and improve the botanical content (ratio of plant-derived components).
The application of coating agents with high oxygen barrier properties inhibits oxidation of the contents and helps reduce food loss. In addition, by eliminating the need to use several different materials to achieve barrier properties, the packaging material can be made with mono-material (single material composition), improving recyclability and reducing the amount of plastic.
In response to the growing problem of marine plastic waste, the use of paper packaging has been promoted in recent years. However, paper is inferior to film in terms of durability and shelf life, and it is extremely difficult to have paper substitute for film. We have developed functional coating agents named "BRITONE" series to complement the functions of water-resistant, oil-resistant, moisture-proof, water-repellent, slip-proof and heat sealability; contributing to the shift to paper packaging.
UV inks, which cure with the energy of ultraviolet light to form a coating film, are energy-saving, environmentally friendly inks that do not require organic solvents, and therefore do not generate VOC. We have developed "Diatone DREAM CURE" series for offset printing, and also products for industrial inkjet printing.
We have developed a de-inking primer that peels and de-inks multi-layer film through alkaline solution treatment to enable film recycling, and a de-inking ink that removes ink from beverage PET beverage bottle labels that makes it possible to collect bottles and films separately.


